Small Animal Super-resolution Ultrasound Imaging System ULTIMUS 9LAB
Category:
Keywords:
Small Animal Super-resolution Ultrasound Imaging System ULTIMUS 9LAB
Product Introduction
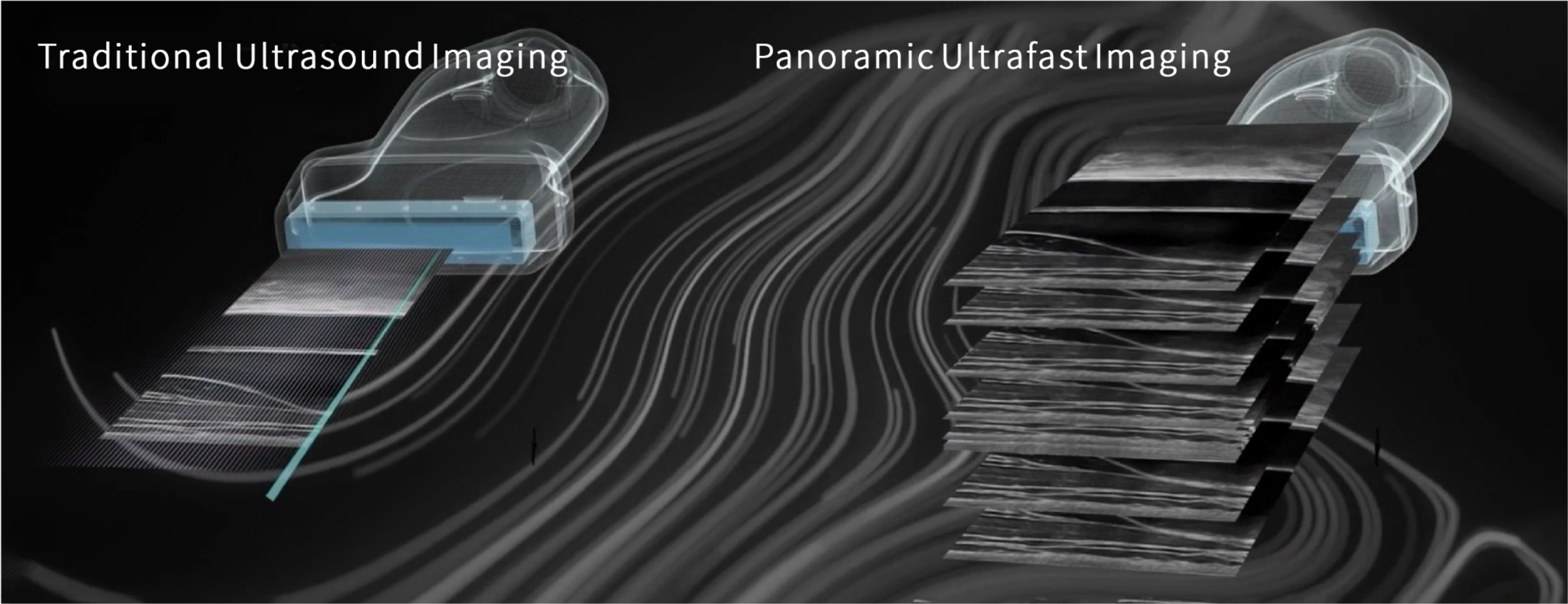
Super-resolution ultrasound imaging is a cutting-edge ultrasound technology. The traditional ultrasound imaging system has a classic contradiction between resolution and penetration. Its resolution limit is limited by the wavelength. The shorter the wavelength, the significantly increased ultrasonic absorption, which seriously limits its imaging. depth. Traditional ultrasonic resolution is around 100 microns. Ultrasound super-resolution imaging has at least a ten-fold increase in resolution compared with traditional ultrasound, while maintaining the penetration and field of view of traditional ultrasound imaging systems. On the premise of non-invasive, it brings opportunities for dynamic imaging of blood vessels with higher temporal resolution. It has broad application prospects in the research fields of diseases closely related to the microvascular system, such as cancer, neurological diseases, and kidney diseases.
The Sixth Generation MUSE Ultrasound Imaging Platfor
- Plane wave technology
- Frame rates up to 20000Hz per second
- Spatial resolution improved ≥10times
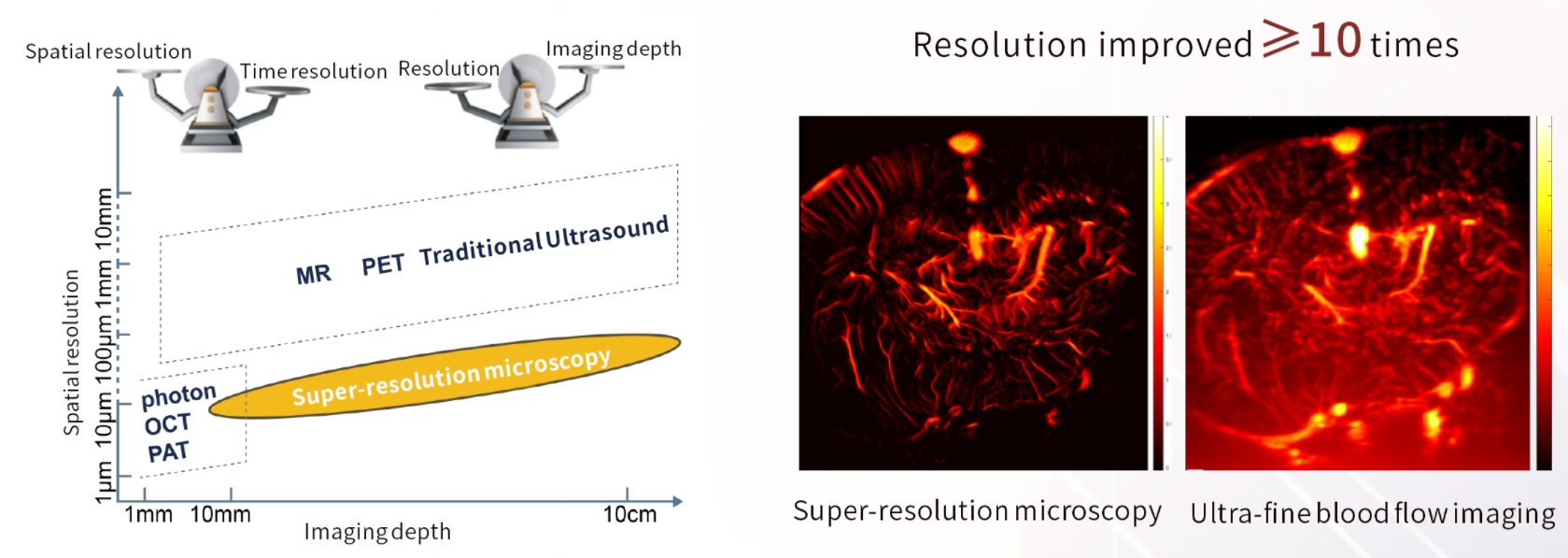
Breaking Traditional Boundaries Resolution improved > 10 times
BeingSuperior To FunctionalMagnetic Resonancelmaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRl) is the "gold standard" fordeep brain imaging in humans. The Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent effect (BOLD) is the basis for its detec-tion of brain function signals. But its limited temporal and spatial resolution of FMRI makes it of limited use when observing small ani-mals,especially mice.The change in blood oxygen-ation levelis actually caused by the change of locacerebral blood flow,and the change oflocal cerebralblood flow is inseparable from the local brain func-tion activity
The SMF function ofULTIMUS 9LAB can replace the change of brain activity by detectingthechange of cerebral blood flow,and has the following characteristics:
- real time imaging
- ≤1ms ultra-high time resolution
- 30um high spatial resolution
- Up to 100 times more sensitive than traditionalultrasoundimaging
- single scan imaging
- Awake and active animal imaging
Ultra Resolution Microscopy imaging(URM)-Advanced Microvascularlmaging
Ultra Resolution Microscopy imaging(URM) injects microbubbles into blood vessels asa means of positioning, and monitors the movement of each microbubble in blood vessels to obtain the corresponding vascular morphology and hemodynamic parameters.This enables high-definition imaging of the microvasculature
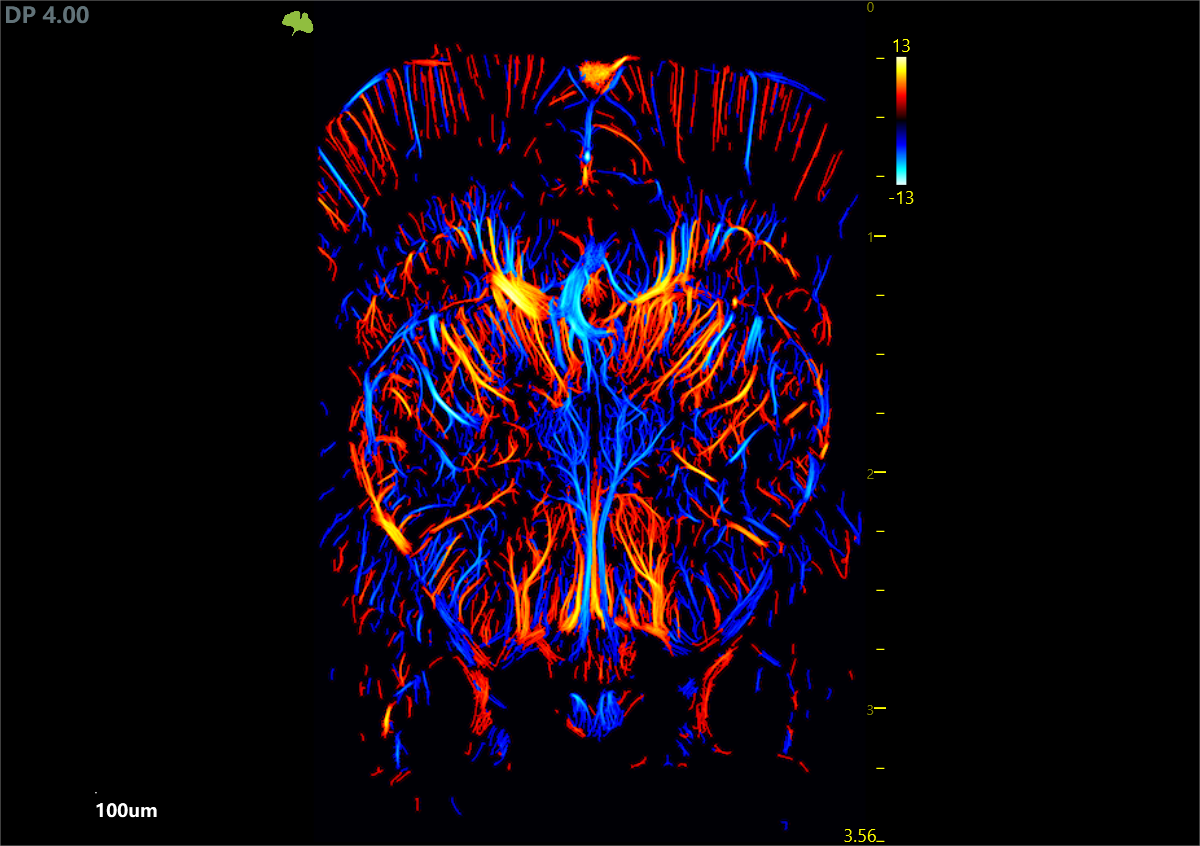
Blood flow dynamic diagram of craniotomy rat brain
Super Micro Flow (SMF)—Observing Cerebral Blood Flow in Real Time
Superfine flow imaging (SMF) monitors brain functional activities by monitoring real-time blood flow changes in brain regions. For example, during the epileptic seizure, the blood perfusion of the epileptogenic focus is increased, and the perfusion volume is decreased between the seizures.
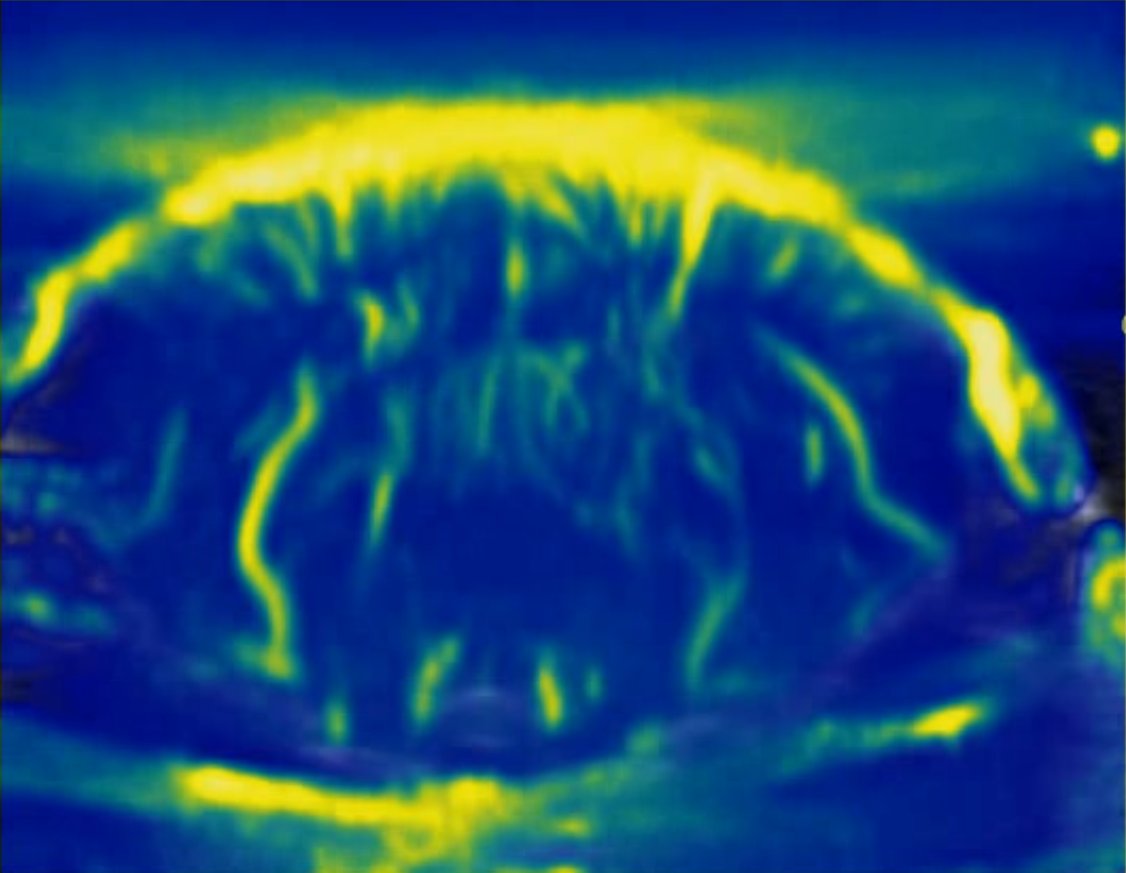
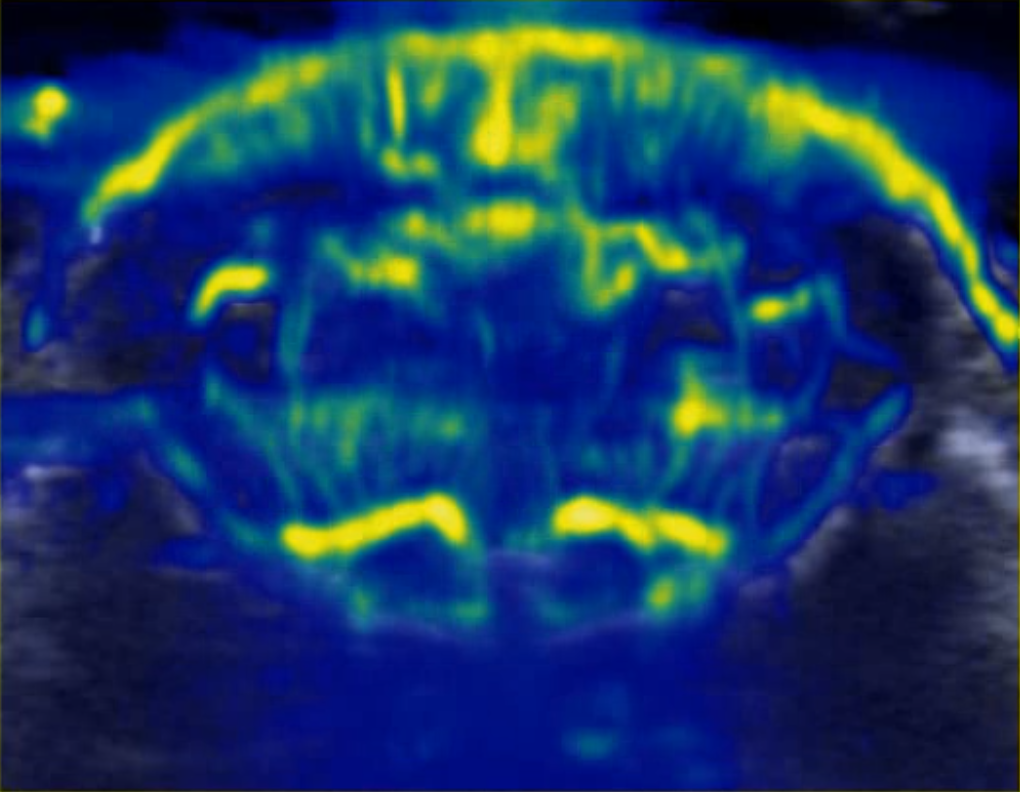
Transcranial image of mouse brain without angiography Transcranial image of mouse brain with angiography
Brain Monitoring in Awake Animals—Precise and Free
ULTIMUS 9 LAB can be used with Neurotar air float cages , no matter where your animals are,whatever it is, whether it's awake or asleep, freely moving or resting, it delivers excellent results. This means you are not limited to studying anesthetized animals. At the same time, Neurotar's behavioral observation system can provide more possibilities for brain researchers.

ZOOM-High Resolution Vascular Imaging
The 30μm microscopic imaging of fine blood flow is just the beginning , and the ZOOM function will allow us to go further, realize the true micron-level blood vessel imaging, and quantify the blood flow velocity in the mm/s range.
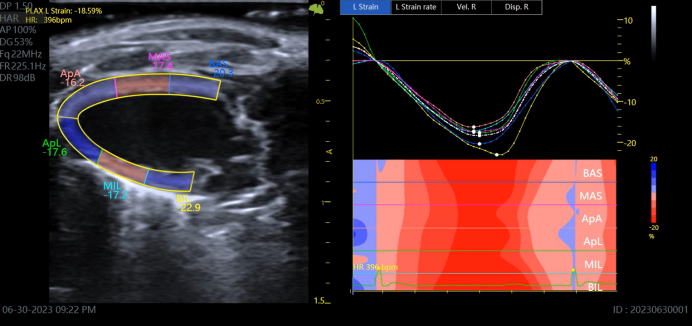
Strain imaging
Echocardiography is currently the primary method used to assess cardiac structure and function, and traditional echocardiographic techniques are relatively insensitive to early or later changes in cardiac function. Cardiogram Strain Analysis (Strain) for Early Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease Models Cardiac tracking-based strain analysis (Strain) of left ventricular function can detect myocardium more sensitively than traditional echocardiographic measurements. Global changes in cardiac function after infarction can also identify early diagnostic differences in the myocardial infarct area and standard cardiac therapy. Siphon tracking-based strain analysis (Strain) represents a new method for relatively high sensitivity and more sensitive detection of cardiac phenotypes.
High-Definition Fast Contrast
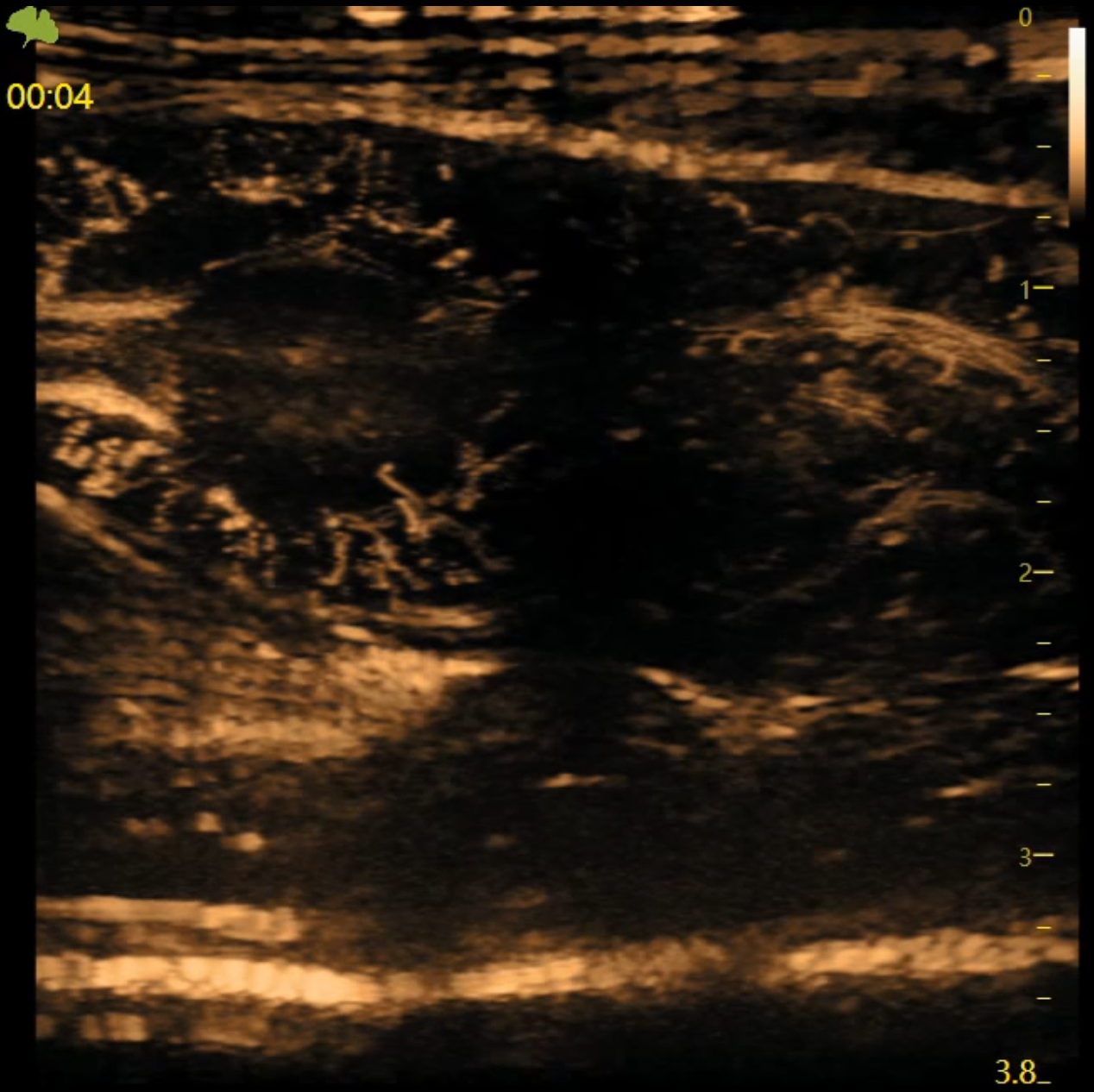


On the basis of panoramic ultra-fast imaging , the high-definition fast contrast technology has doubled the frame rate of traditional contrast, and can achieve high-definition fast contrast at 300 frames per second. Higher time resolution and spatial resolution are obtained , which can really allow researchers to see the process changes of radiography from scratch,and more realistically show the process of radiography .
Tumor Cavitation
Low-intensity ultrasound treatment avoids the side effects of thermal damage caused by high-intensity ultrasound,monitors and regulates the cavitation intensity in the treatment target area, and monitors the treatment process in real time through small animal ultrasound images to achieve precise treatment . It provides reliable equipment support for solving the major medical science problem of hypoxic solid tumor therapy resistance.
MUSE Ultrafast Soft Beamforming Platform—vFlash
vFlash has newly added a curative effect evaluation process,which can introduce multi-modal imaging evaluation, and automatically select the same evaluation area as that before cavitation through section guidance,and compare perfusion characteristics to form a more effective curative effect evaluation.


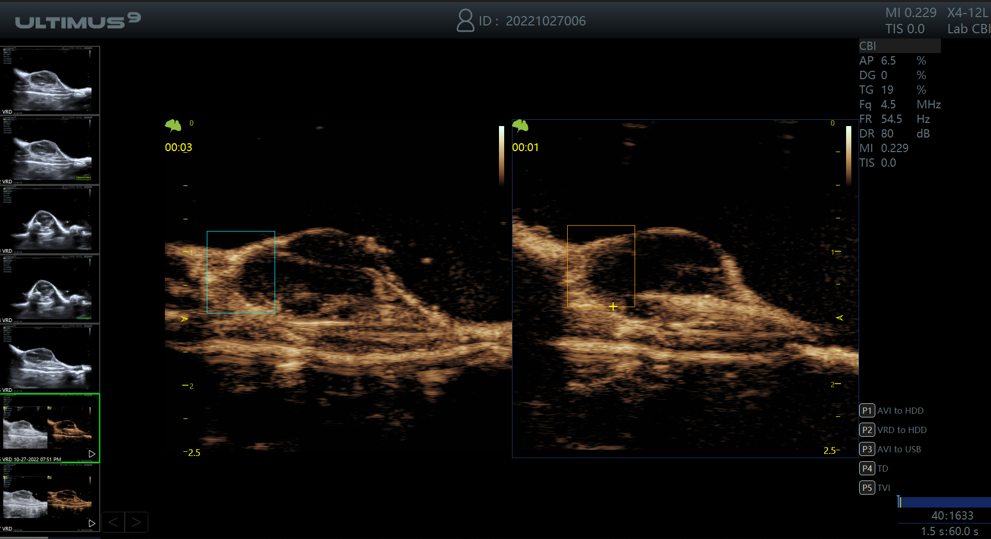
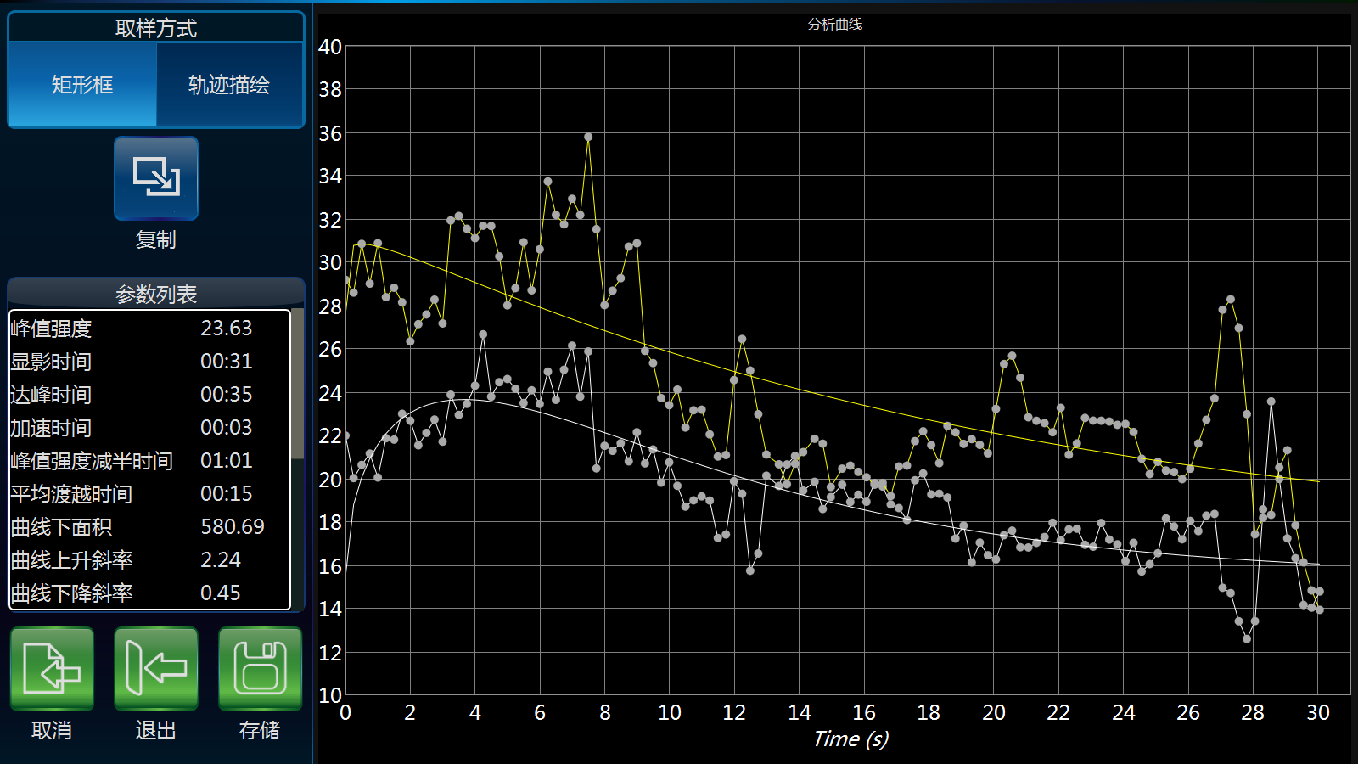
Time-intensity curve analysis allows users to analyze the perfusion process of the region of interest from 9 different perspectives

| Work in time | WIT | Time to peak | TTP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acceleration time | ATT | Mean transit time | MTT |
| Work out timel | WOT | Peak intensity | PI |
| Area under the curve | AUC | Work in rate | WIR |
| Work out rate | WOR |
Traditional Ultrasound Applications

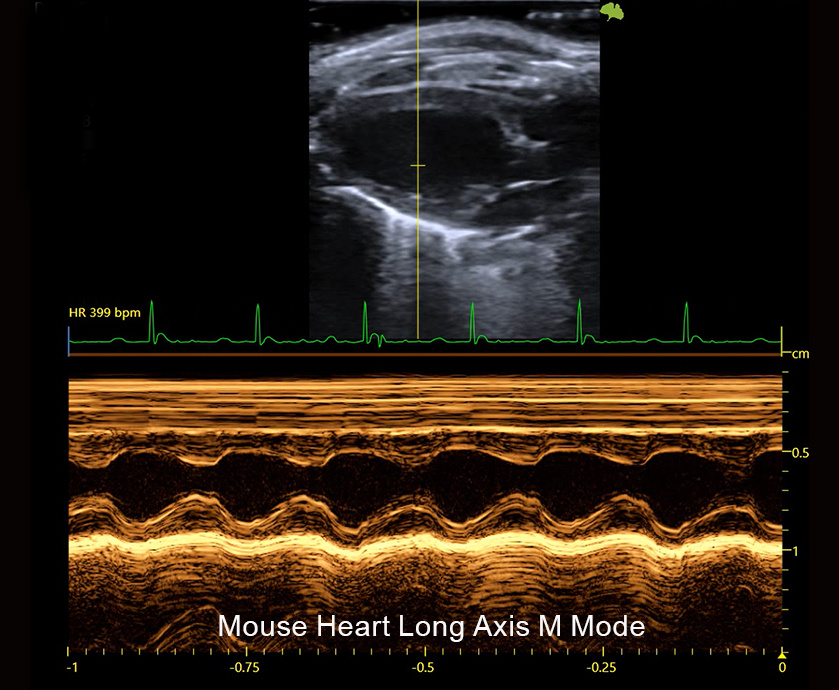
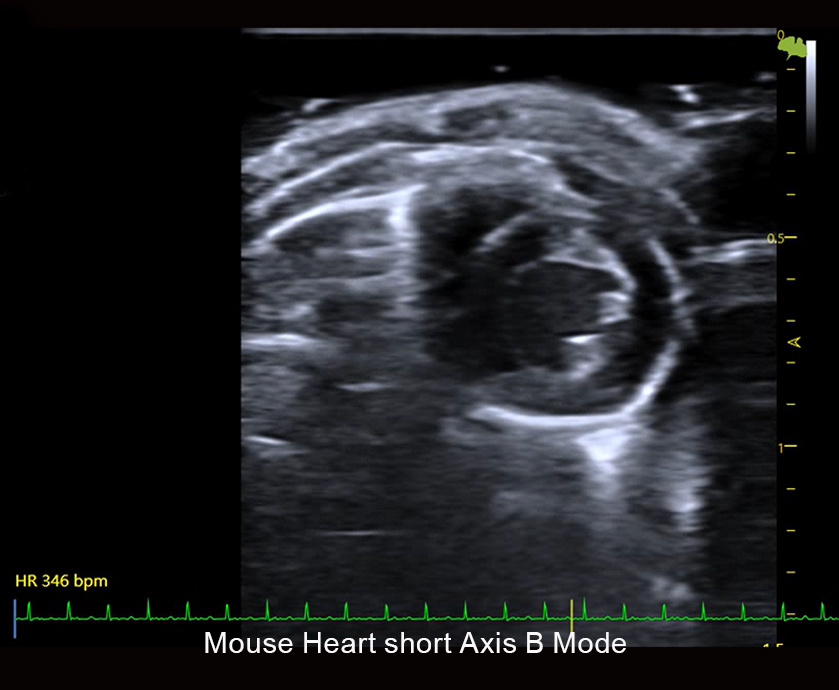
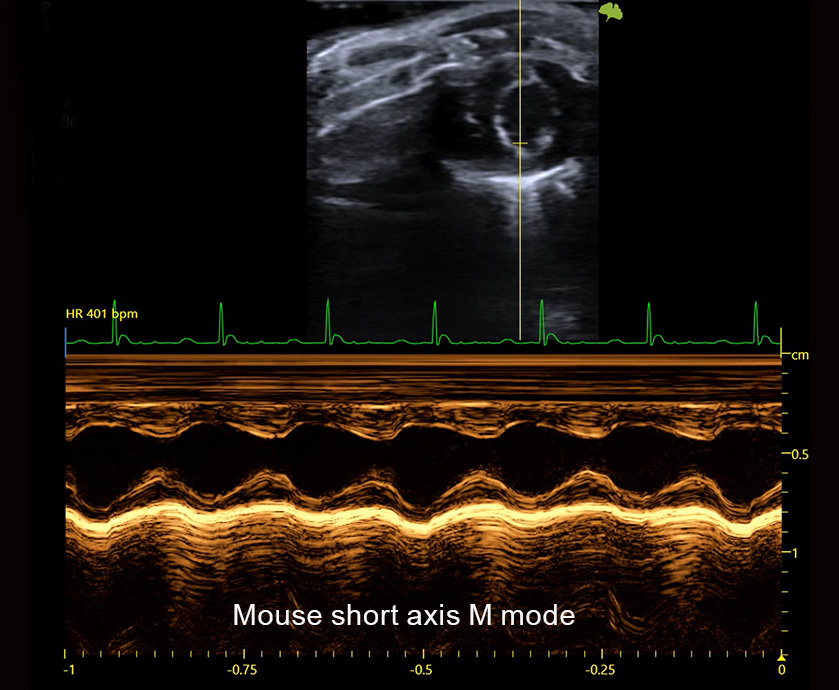
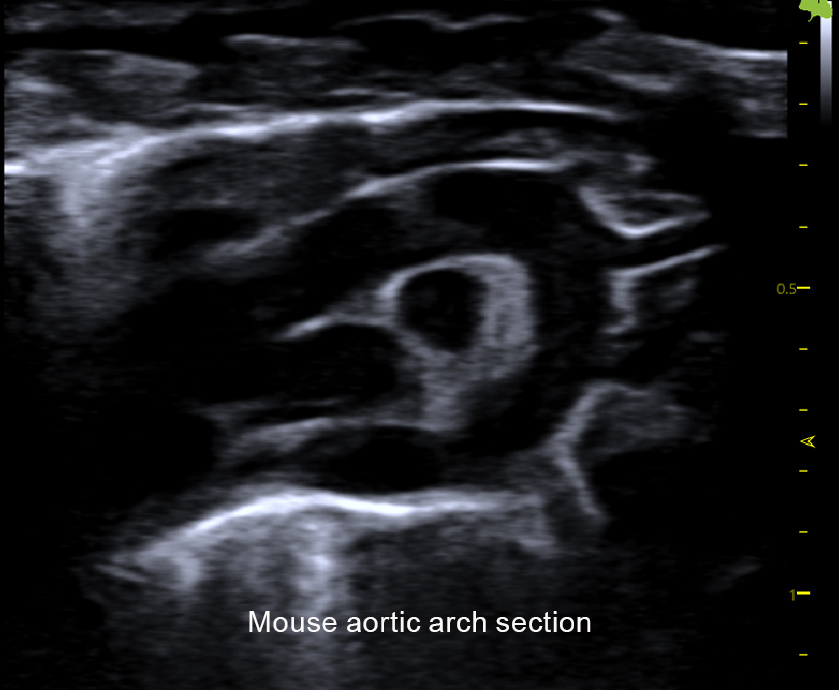
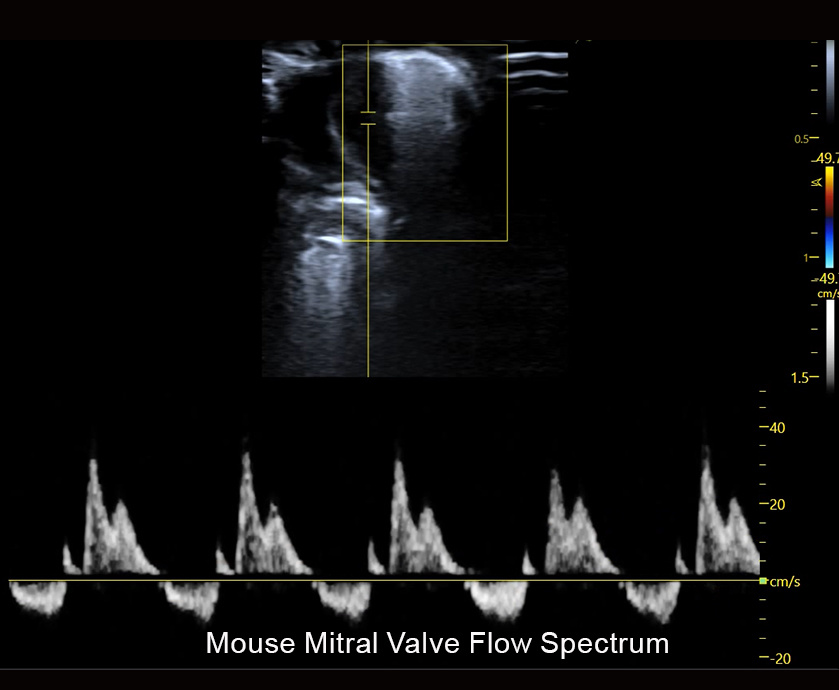
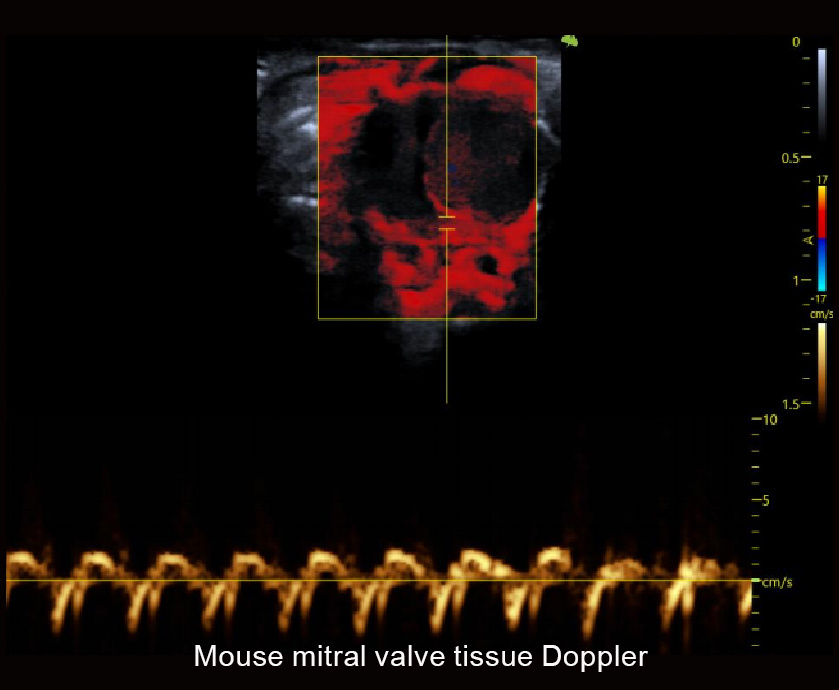


Neuroscience
Cerebral Blood Flow Imaging
Super-resolution ultrasound imaging can not only display the overall situation of micro-blood flow and microcirculation at the micron level, but also solve the problem of displaying the details of the micro-vascular network . It can also be used to measure micro-blood flow velocity, direction, distribution, vessel shape (such as tortuosity and other indicators) and its diameter, etc. It improves the clinical understanding of the microvascular system and the construction of disease models.
Stroke
The geometrical configuration of the middle cerebral artery, vessel diameter and tortuosity, anatomical variation and integrity of the circle of Willis and other vascular geometric factors are related to the distribution of intracranial atherosclerotic plaques. Vessel shape matters for intracranial atherosclerosis-related stroke.
Epilepsy
Ultrafine blood flow imaging SMF can capture real-time changes in blood flow in the brain, suggesting the onset of epilepsy.
Alzheimer's Disease
Microbubbles are widely used in contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging. In super-resolution ultrasound imaging applications, it opens the door to non-invasive assessment of stroke, vascular occlusion,and neurovascular health.Ultrasound imaging can rapidly measure and reconstruct global cerebral vessels and blood flow in the mouse brain, which can be used to study the neurovascular mechanisms of diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.
Mouse Transcranial Ultrasound Imaging
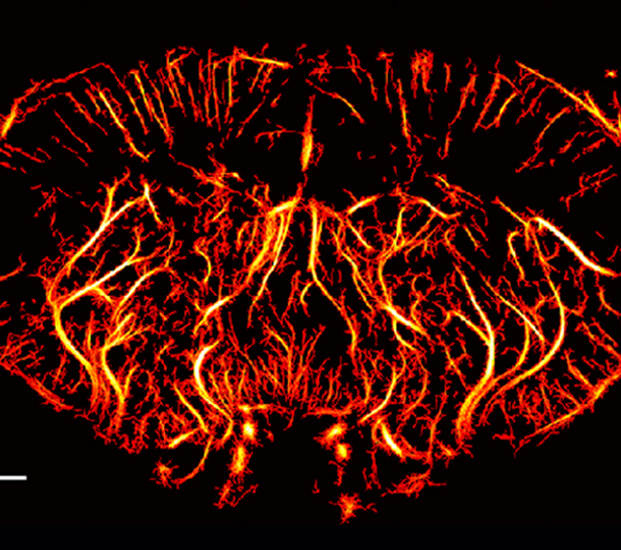
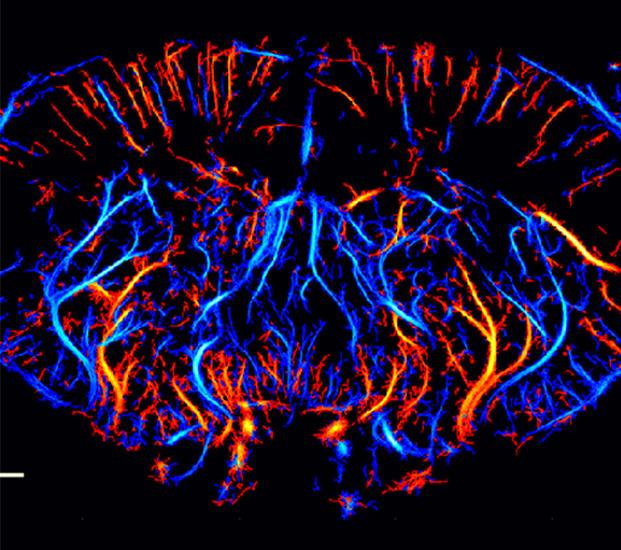
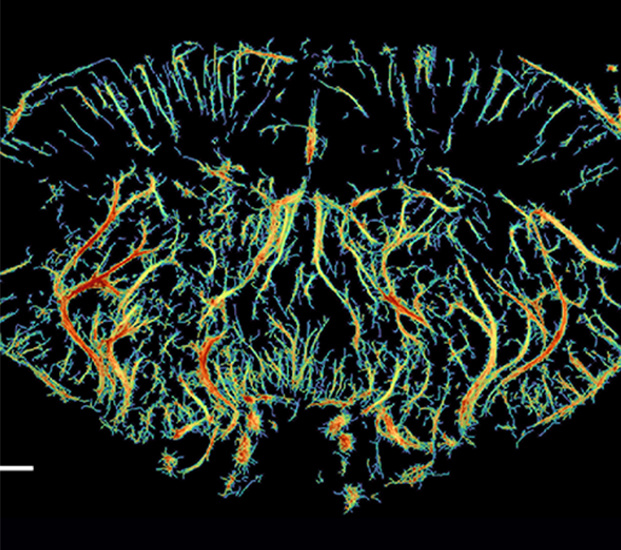
Rat Craniotomy Ultrasound Imaging


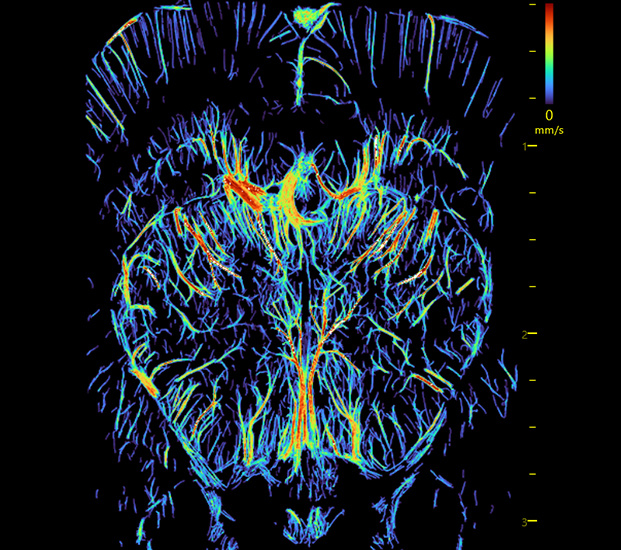
Stroke Rat with Left Side Ligation Ultrasound Imaging
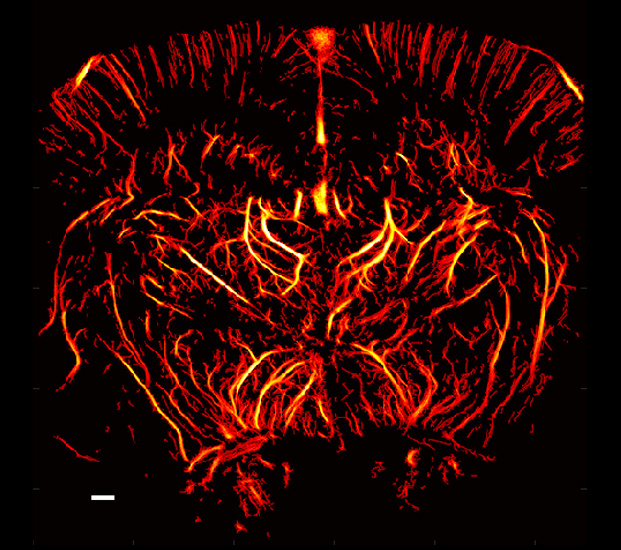
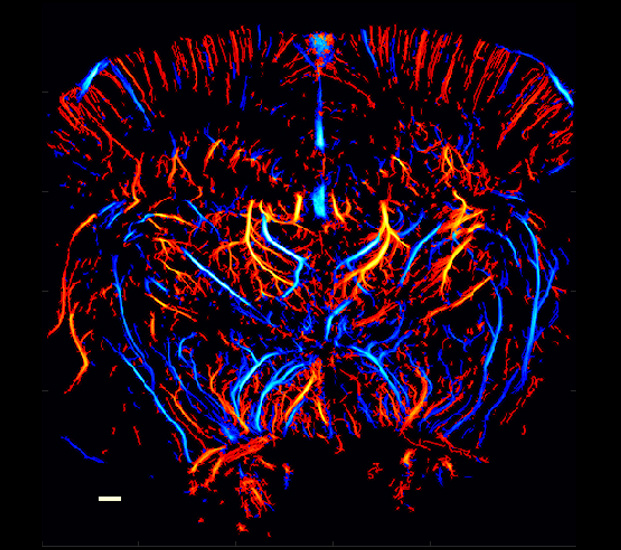
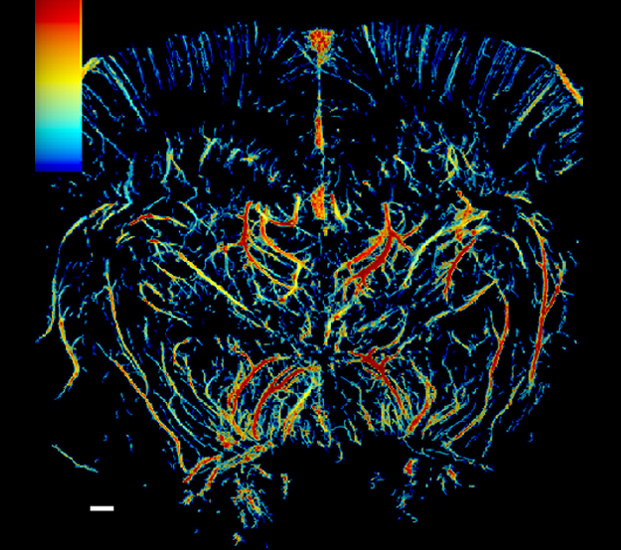
Super-resolution blood vessel density distribution map/Super-resolution blood flow direction map/Super-resolution blood velocity map
Tumor
The growth of neonatal blood vessels is a striking feature that distinguishes early cancer tissue from normal tissue, and is recognized as an important biomarker for the diagnosis of cancer, detected by super-resolution microscopy imaging at an early stage and during tumor progression with higher resolution and sensitivity Microvascular hemodynamics and morphological changes.
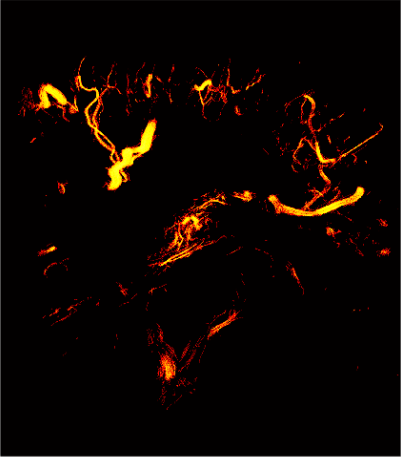

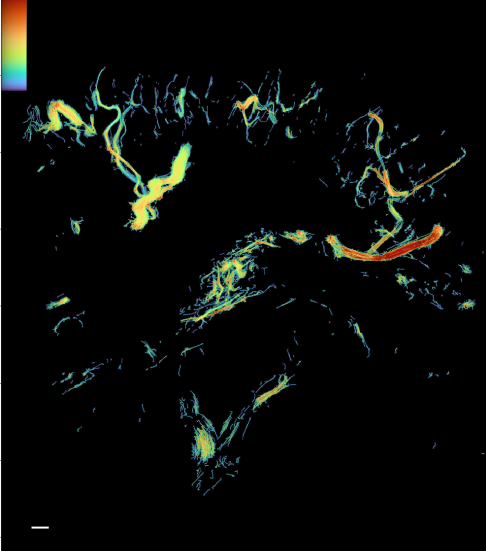
Super-resolution blood vessel density distribution map/Super-resolution blood flow direction map/Super-resolution blood velocity map



Normal flow chart /Ultra fine blood flow map/Super-resolution micrograph
Kdney Diseases
Kidney microvascular injury is related to most kidney diseases. Super-resolution ultrasound imaging can conduct real-time non-invasive long term continuous observation of kidney microvessels in living animals through its ultra-high resolution characteristics, providing a new method for longterm monitoring of kidney diseases.It provides new ideas for ongoing kidney disease research.


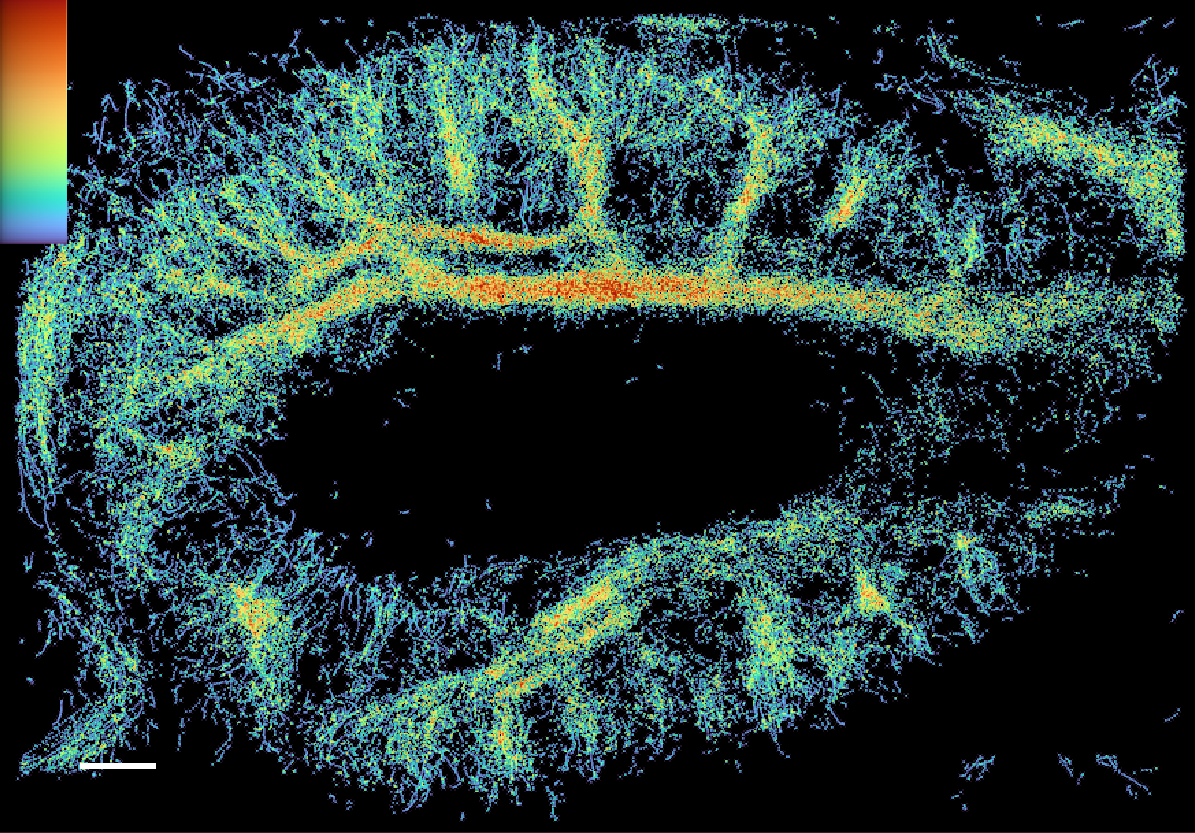
Myocardial Blood Flow
In the field of coronary microcirculation function research,it has been desired to directly evaluate the coronary microcirculation system.However ,for a long time,due to the motion characteristics of the heart and the diameter of the blood vessels,coronary microvessels cannot be directly evaluated by imaging examinations.Coronary microvascular function can only be assessed by a battery of invasive and noninvasive tests.The ultrasonic super-resolution imaging system, due to its ultra-high frame rate of 20,000 frames per second and its micron-level ultra-high resolution,makes it possible to directly study the myocardial coronary artery microcirculation system.
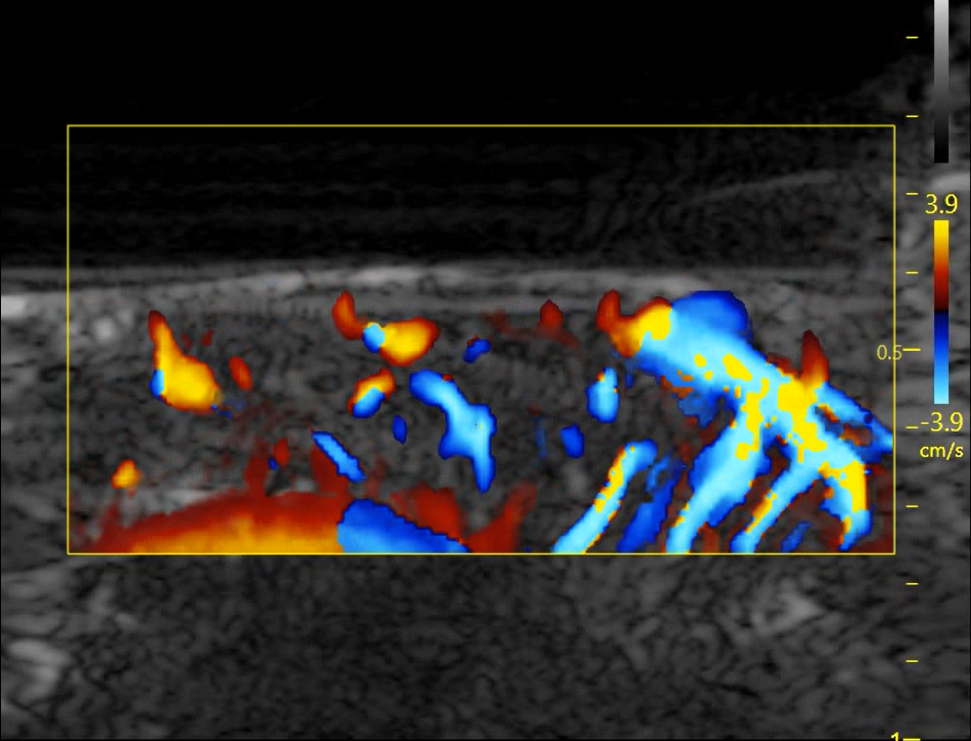

Myocardial blood flow imaging in rats
Need help?
Let's ask your questions




